Stackup Design
Table of Contents
Stackup involves the size and organization of the different PCB layers to make up an efficiently working circuit board. These involve different types of layers and should be done with a set of rules, to ensure your designed PCB retains the signal integrity, quality, and is cost-efficient throughout the production processes, and throughout its lifetime.
Stackup Design
The design of how PCB layers are positioned, along with their dimensions and other deciding parameters is known as stackup. Designing how the stackup of a multilayered PCB is extremely important as they decide on how the PCB process sequence were to be carried out, how its impedance is, and what manufacturing materials are used. [STACKUP DESIGN IMAGE HERE]
- Your stackup design should consider these factors:
- Board thickness of each layer
- Dielectric thickness of each layer
- Overall PCB thickness
- Arrangement selection of GND reference layer
- The adjustment for the calculated and real impedance.
- The thickness of the solder and solder mask layers
The stackup design ensures the best working performance for multi layer circuit boards. The configuration of multilayer PCB must be symmetrical on both sides, taking the example of the simplest multilayer boards:
- 4-layer PCB: TOP-GND-VCC-BOT or change the 2 middle layers to GND-SIG/PWR-SIG/PWR-GND
- 6-layer PCB: TOP-GND-SIG-VCC-GND-BOT
During the process of designing your multilayer PCBs, there are several board material choices present:
- Phenolic paper-based copper clad laminate (FR1/FR2)
- Composite base copper clad laminate (CEM-1, CEM-3)
- Glass fiber cloth copper clad laminate (FR4)
- Aluminum plate
- Ceramic substrate
- PP prepreg (Prepreg)
These choices of materials can be used for both prototyping and mass production. However, the number of layers, board thickness, and copper weights limitations for the two stages are different.
| Prototyping | Mass production | |
|---|---|---|
| Layers | Up to 40 | Up to 20 |
| Thickness | 0.15 - 6.40 mm | 0.20 - 5.00 mm |
| Inner copper weight | 0.5 - 10 oz | 0.5 - 4.0 oz |
| Outer copper weight | 0.3 - 11 oz | 0.5 - 5.0 oz |
The inner copper weight is the substrate/RCC’s specific copper thickness, and the outer copper weight is the added copper layer done by the process of electroplating. For example, the term 0.5 oz+plated means the initial 0.5 inner copper weight is to be electroplated by an additional of 0.5 oz (the standard parameter of copper plating). In this example, the total outer copper weight will amount to 1.0 oz.
The general stackup design is done in this format:
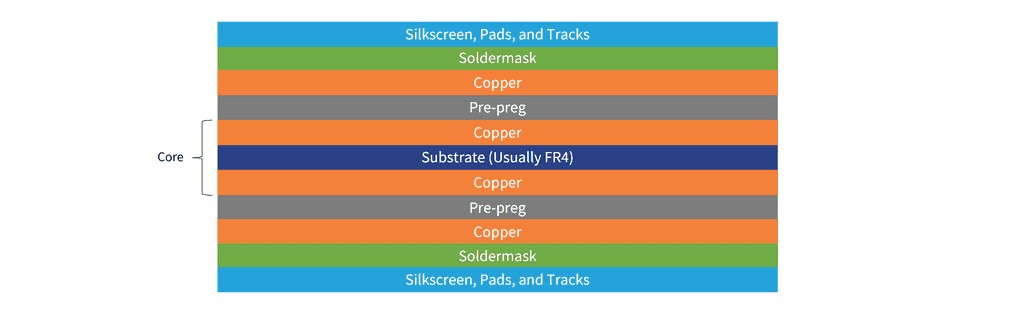
- Substrate should be used as the base layer. If there are several substrates used, all of them must be pressed together first.
- Above and below the substrate layer should be 1 layer of prepreg
- Covering these prepreg layers, 1 sheet of copper or PP-copper layer (a preprocessed combined PP and copper), added with 2 layers of laminating layer.
- After this, the layering will be continued by 2 layers of copper (or PP-copper) layer followed by 2 layers of the laminating layer, until the required number of layers is obtained.
